Photodiode Detector, PD detector
Product Introduction
Kinheng can provide scintillator detectors based on PMT, SiPM, PD for radiation spectrometer, personal dosimeter, security imaging and other fields.
1. SD series detector
2. ID series detector
3. Low energy X-ray detector
4. SiPM series detector
5. PD series detector
|
Products |
|||||
|
Series |
Model No. |
Description |
Input |
Output |
Connector |
|
PS |
PS-1 |
Electronic module with socket, 1”PMT |
14 Pins |
|
|
|
PS-2 |
Electronic module with socket& high/ low power supply-2”PMT |
14Pins |
|
|
|
| SD |
SD-1 |
Detector. Integrated 1” NaI(Tl) and 1”PMT for Gamma ray |
|
14 Pins |
|
|
SD-2 |
Detector. Integrated 2” NaI(Tl) and 2”PMT for Gamma ray |
|
14Pins |
|
|
|
SD-2L |
Detector. Integrated 2L NaI(Tl) and 3”PMT for Gamma ray |
|
14 Pins |
|
|
|
SD-4L |
Detector. Integrated 4L NaI(Tl) and 3”PMT for Gamma ray |
|
14 Pins |
|
|
| ID |
ID-1 |
Integrated Detector, with 1” NaI(Tl), PMT, electronics module for Gamma ray. |
|
|
GX16 |
|
ID-2 |
Integrated Detector, with 2” NaI(Tl), PMT, electronics module for Gamma ray. |
|
|
GX16 |
|
|
ID-2L |
Integrated Detector, with 2L NaI(Tl), PMT, electronics module for Gamma ray. |
|
|
GX16 |
|
|
ID-4L |
Integrated Detector, with 4L NaI(Tl), PMT, electronics module for Gamma ray. |
|
|
GX16 |
|
|
MCA |
MCA-1024 |
MCA, USB type-1024 Channel |
14 Pins |
|
|
|
MCA-2048 |
MCA, USB type-2048 Channel |
14Pins |
|
|
|
|
MCA-X |
MCA, GX16 type Connector-1024~32768 channels available |
14Pins |
|
|
|
|
HV |
H-1 |
HV Module |
|
|
|
|
HA-1 |
HV Adjustable Module |
|
|
|
|
|
HL-1 |
High/Low Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
HLA-1 |
High/Low Adjustable Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X-1 |
Integrated detector-X ray 1” Crystal |
|
|
GX16 |
|
S |
S-1 |
SIPM Integrated Detector |
|
|
GX16 |
|
S-2 |
SIPM Integrated Detector |
|
|
GX16 |
|
SD series detectors encapsulate crystal and PMT into one housing, which overcomes the hygroscopic disadvantage of some crystals including NaI(Tl), LaBr3:Ce, CLYC. When packaging PMT, internal geomagnetic shielding material reduced the influence of geomagnetic field on the detector. Applicable for pulse counting, energy spectrum measurement and radiation dose measurement.
| PS-Plug Socket Module |
| SD- Separated Detector |
| ID-Integrated Detector |
| H- High Voltage |
| HL- Fixed High/Low Voltage |
| AH- Adjustable High Voltage |
| AHL- Adjustable High/Low Voltage |
| MCA-Multi Channel Analyzer |
| X-ray Detector |
| S-SiPM Detector |
Different Materials’ Performance Parameters
| Scintillator material |
CsI(Tl) |
CdWO4 |
GAGG:Ce |
GOS:Pr/Tb Ceramic |
GOS:Tb Film |
| Light yield(photons/MeV) |
54000 |
12000 |
50000 |
27000/45000 |
145% of DRZ High |
| Afterglow(after 30ms) |
0.6-0.8% |
0.1% |
0.1-0.2% |
0.01%/0.03% |
0.008% |
| Decay time(ns) |
1000 |
14000 |
48, 90, 150 |
3000 |
3000 |
| Hygroscopic |
Slightly |
None |
None |
None |
None |
| Energy range |
Low energy |
High energy |
High energy |
High energy |
Low energy |
| Overall costs |
Low |
High |
Middle |
High |
Low |
PD Performance Parameters
A. Limit parameters
|
Index |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
| Max Reverse Voltage |
Vrmax |
10 |
v |
| Operation temperature |
Top |
-10 -- +60 |
°C |
| Storage temperature |
Tst |
-20 -- +70 |
°C |
B. PD photoelectric characteristics
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Term |
Typical value |
Max |
Unit |
| Spectral response ranges |
λp |
|
350-1000 |
- |
nm |
| Peak response wavelength |
λ |
|
800 |
- |
nm |
| Photosensitivity |
S |
λ=550 |
0.44 |
- |
A/W |
|
λp=800 |
0.64 |
||||
| Dark current |
Id |
Vr=10Mv |
3 - 5 |
10 |
pA |
| Pixel capacitance |
Ct |
Vr=0,f=10kHz |
40 - 50 |
70 |
pF |
PD Detector Drawing
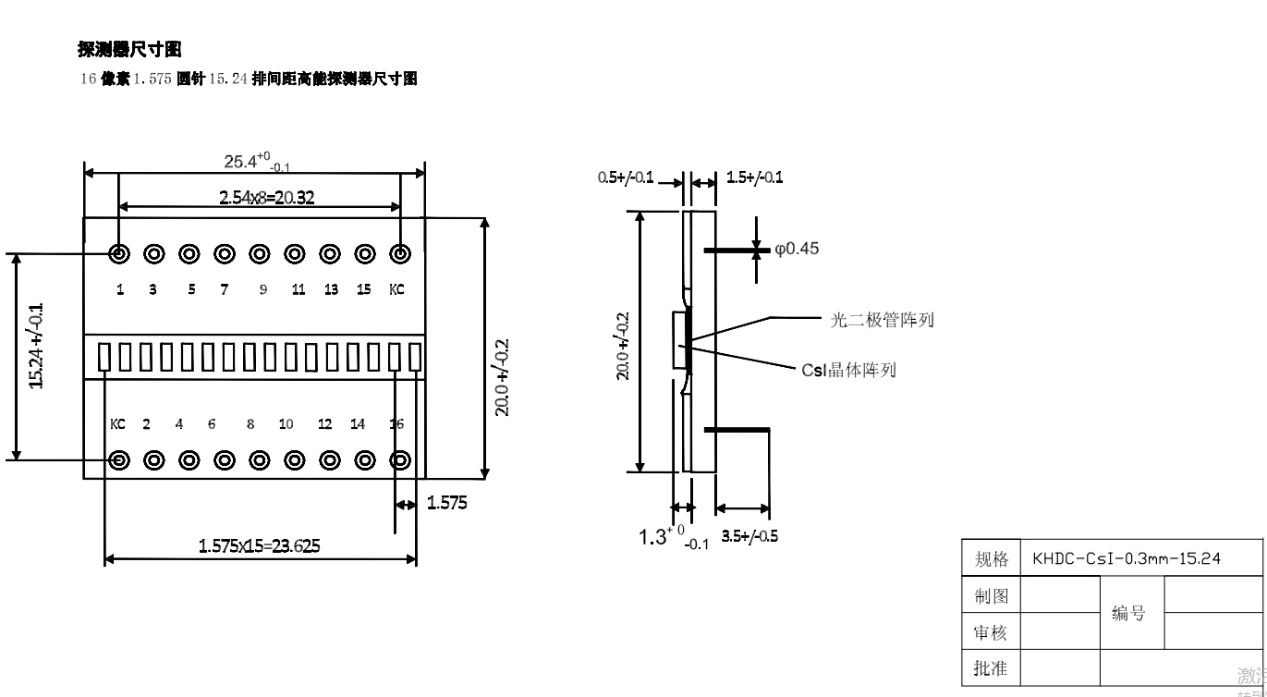
(P1.6mm CsI(Tl)/ GOS:Tb Detector)
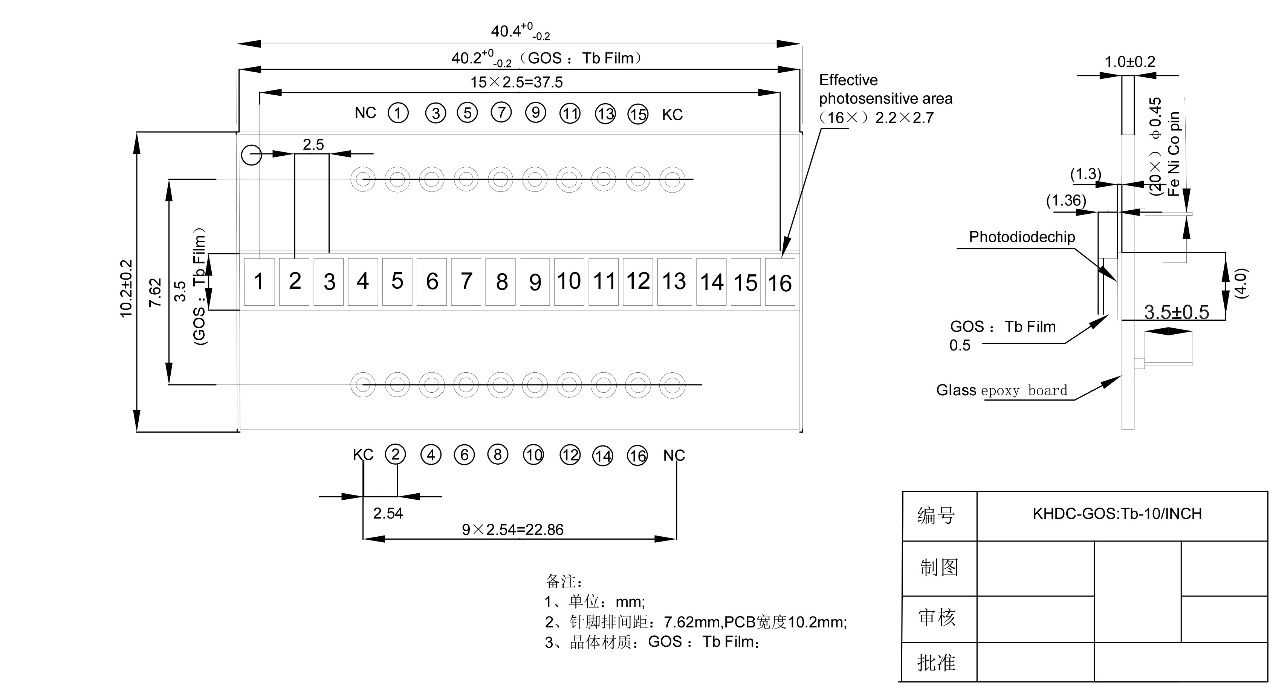
(P2.5mm GAGG/ CsI(Tl)/CdWO4 Detector)
PD Detector Module

CsI(Tl) PD detector

CWO PD detector

GAGG: Ce PD detector

GOS:Tb PD detector
Application
Security inspection, systematic process of examining and assessing individuals, objects, or areas to ensure compliance with safety protocols and regulations, as well as to identify and mitigate potential security risks. It involves inspecting and scrutinizing various aspects, Security inspections are conducted in a variety of settings, including airports, seaports, governmental buildings, public events, critical infrastructure facilities, and private businesses. The main objectives of security inspections are to enhance the safety and security of individuals and assets, prevent the entry of prohibited items or dangerous substances, detect potential threats or criminal activities, and maintain law and order.
Container inspection, In the context of container inspection, detectors are used to identify any potential radioactive materials or sources that may be present within a container. These detectors are typically placed at key points in the container inspection process, such as entrances or exits, to screen and monitor the contents of containers. container inspection for various purposes, including: Radiation monitoring, Identifying radioactive sources, Preventing illicit trafficking, Ensuring public safety, etc.
Heavy vehicle inspection, refers to a specialized device or system used to identify and evaluate various aspects of heavy vehicles, such as trucks, buses, or other large commercial vehicles. These detectors are commonly used at checkpoints, border crossings, or inspection stations to ensure compliance with safety, regulatory, and legal requirements.
NDT, detector used in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) refers to a device or sensor that is employed to detect and measure various types of discontinuities or flaws in materials or structures without causing any damage to them. NDT techniques are extensively used in industries like manufacturing, construction, aerospace, automotive, and more to assess the integrity, quality, and reliability of components or materials.
Ore screening industries, can refer to a device or system used to identify and separate valuable minerals or materials from the ore during the screening process. These detectors are designed to analyze the physical and chemical properties of the ore and detect specific characteristics or elements of interest. X-ray or radiometric detectors is the choice of detector in ore screening industries depends on the specific composition of the ore, the desired target minerals, and the efficiency and accuracy required in the screening process. These detectors play a crucial role in maximizing the extraction of valuable minerals, reducing waste, and optimizing the overall ore processing operations.















